Radiation
Radiation
Black body
- A black body is an ideal emitter
- Energy radiated can be calculated using Stefan-Boltzmann Law
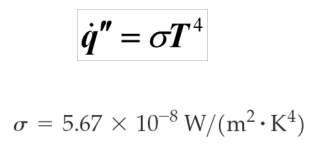
- The radiation emitted by the body, , is referred to as the black body emission and is often denoted by Eb . It is the total energy radiated over all wavelengths.
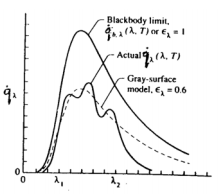
- Eb,λ , is the monochromatic emissive power.
- At any temperature, Eb,λ has a maximum value at a particular wavelength
- As the temperature increases, the maximum occurs at shorter wavelengths (Wein's Law)
- The visible range extends from about 0.7 microns (red) to 0.4 microns (violet)
- The peak for solar energy lies within this range
- Colour of star depends on temperature of surface (Wein's Law)
- Cold stars red. Hot stars blue (Wein's Law)
Grey body
- As an engineering approximation, surfaces are often assumed to be grey, and the radiation emitted is calculated using:
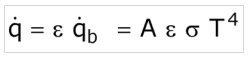
Transmission, absorption, and reflection
- τ = fraction of radiation transmitted
- α = fraction of radiation absorped
- ρ = fraction of radiation reflected
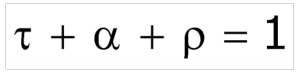
- Opaque transmit no radiation
- Reflection may be specular as for mirror or diffuse
- tau, alpha, rho are function of wavelenght, but we approximate with constant value to particular temperature range
Created with the Personal Edition of HelpNDoc: Create cross-platform Qt Help files